- Write With AI in Your Brand’s Voice with GrowthBar - April 21, 2023
- How Long Should a Blog Post Be? [2025] - April 14, 2023
- 13+ Best ChatGPT Prompts for SEOs [2025] - April 14, 2023
Ended soon
If you’re publishing content online and want people to find you—which you surely do—it’s essential you learn about search engine optimization (SEO).
Without optimizing your content for search engines, you’re not going to appear in front of people searching for queries you’re targeting. It’s as simple as that.

But the best part of SEO is…
Even though Google’s algorithm is always changing, the fundamentals have stayed the same. So if you master a few key things, even average bloggers and digital publishers can outrank big, established websites.
Fundamentally, SEO boils down to simply structuring and optimizing your website’s content—pages and blog posts—for visitors and search engines.
To help you do exactly that, we’ve put together this beginner’s guide to SEO. So before you hire an SEO agency, read this.
Table of Contents
What is Search Engine Optimization (SEO)?
SEO stands for “search engine optimization.” Search engines are tools like Google and Bing that we use to find answers and information based on the keywords we type in.
Google dominates the search engine space with a huge 86% market share. So, we’ll be talking about Google for the purpose of this post. But Bing, the second largest search engine, operates in an almost identical way.
The simplest way to explain SEO to someone with no experience in internet marketing or blogging is as follows:
SEO is the process of improving your website, so your pages appear higher in the search results for your desired keywords.
If you’re a moving company in Los Angeles, imagine ranking #1 or #2 in Google’s search engine results page (SERP) for the query “moving company in Los Angeles.” You would get a lot of free leads, right?
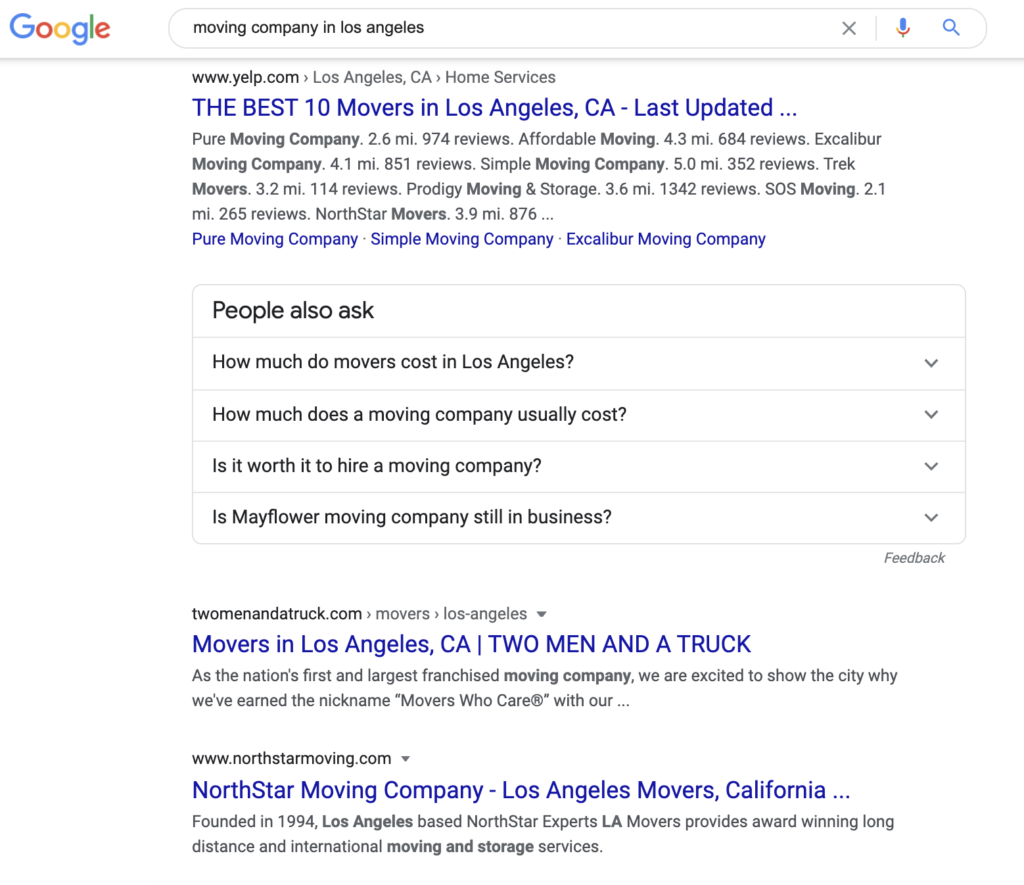
Sounds simple enough, doesn’t it? Well, it is, as you’re going to find out.
Why is SEO So Important?
Most advertising channels are super expensive. And you pay on a cost-per-click (CPC) or cost per 1,000 views (CPM) model.
With SEO, you only pay for the cost of making web pages and blog articles. You don’t pay for every click or view, which makes SEO the most cost effective marketing channel there is.
If you can master SEO and make articles rank at-will, you’re going to be able to build a repeatable, scalable, and profitable business.
How Do Search Engines Work?
Search engines possess powerful algorithms that weigh hundreds of factors to rank every page on the internet.
As a digital publisher or internet marketer, your end goal is to satisfy the search engines so that you rank on page 1 of the Google search engine results page (SERP) for any given query.
So, it makes sense to understand how search engines work and what they’re looking for, right?
Additional reading: Learn more about Google’s algorithm here.
The Goal of a Search Engine
Believe it or not, a search engine’s goal is similar to yours—to display the most relevant and highest-quality results for any given search query. Surfacing good content is how Google makes money!
If their search results stunk, you’d start your search somewhere else.
So, if you can align your content with what a search engine determines to be the most relevant result, it’s a recipe for success.
If you’re curious to know how a search engine works beneath the hood, it goes something like this:
- Crawling: When you publish an article and make the URL live, you’re giving that page an address to be found. Search engines crawl the internet looking for URLs to add to their database. They send out web crawlers, also called “spiders” or “search engine bots.” Crawlers look at webpages and follow links on those pages, much like you would if you were browsing content on the web. They go from link to link and bring data about those webpages back to Google’s servers.
- Indexing: Once a page has been crawled, it’s added to a search engine’s index. An index is a database of all the URLs their bots have discovered.
- Ranking: Search engines use complex algorithms to rate and rank pages in the search results. They literally use hundreds of signals when rating a webpage, including content relevance, site speed, bounce rate, keyword density, backlinks, and a myriad of other things.
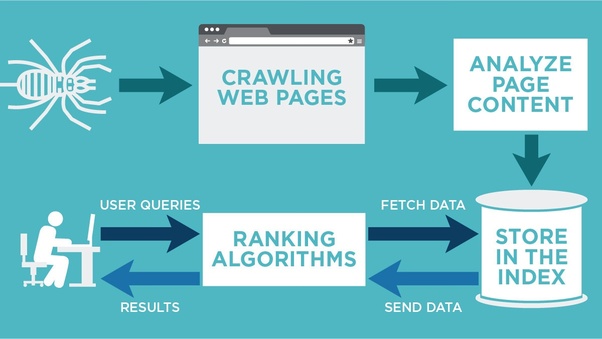
The ranking factors are what digital marketers are most concerned with. By understanding and reverse engineering those factors, you can make your own content reach the top of Google’s search results. Most marketers break SEO out into two major categories:
- On-page SEO
- Off-page SEO
Let’s explore each.
The Two Pillars of SEO: On-Page and Off-Page Optimization
Smart marketers can pick a keyword, create content, game the search engines, and capture leads for that exact keyword. And they usually do it with a combination of on-page and off-page SEO optimization.
- On-Page SEO: This is the practice of optimizing each page for specific keywords you want to rank for. This means writing high-quality content or creating a great experience for your visitors and telling search engines what keywords you want your page to rank for.
- Off-Page SEO: This refers to actions you take off of your site that have SEO implications. For the most part, this relates to backlinking: the art of improving a website’s credibility by garnering backlinks (links pointing to your site from other sites).
Let’s take a closer look at each of these areas and what you can do to optimize your site better.
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO is about:
- Making great content for Googlers
- And presenting your content in a way that Google crawlers can easily read and understand
Remember, search engines want to show users the best content or best answer to their search query. So writing great blog posts or making super useful web pages is the most important first step.
However, the harsh reality is that you can write the best, most informative, detailed article on the planet—but if you’re not optimizing it for search engines, it’s not going to be seen. Here’s a sad SEO statistic for you: 90.63% of all content indexed by Google gets no traffic.
To give your content the very best chance of ranking highly on page one, here are the most important on-page factors to focus on:
1. Keyword Research
Keywords are Google search queries. They’re the words someone types into Google when they’re searching for something.
The first (and probably most important) step in ranking for blog topics is to select a list of target keywords for your web page or blog post. The art of finding those keywords is called keyword research.
For example, if you’re interested in buying a Chromebook, you might search for:
- “Best Chromebook”
- Or, “Best Chromebook under $500” if that’s your budget.
- Or, you may even be more specific if you have an idea of what you’re after. Such as “Lenovo Chromebook c330 review.”
If you put yourself on the other side, as a business selling Chromebooks, you want to appear as high in the search results as possible.
But of course, some keywords are more competitive than others. “Head terms” like “Chromebook” have millions of articles. Trying to rank for that keyword means you’ll be competing with PC Mag, Amazon, Best Buy, and Google itself!
But long-tail queries like the ones below are much less competitive:
- “Best Acer Chromebooks under $500.”
- “Chromebooks for college students.”
- “How much do used HP Chromebooks cost?”
You’ll quickly come up with a long list of queries by doing this. The next step is to verify there is search volume for these queries and determine how difficult they will be to rank for.
Great SEO tools (more on that below) will have a keyword difficulty score, enabling you to determine which keywords are the most worth pursuing in an SEO strategy.
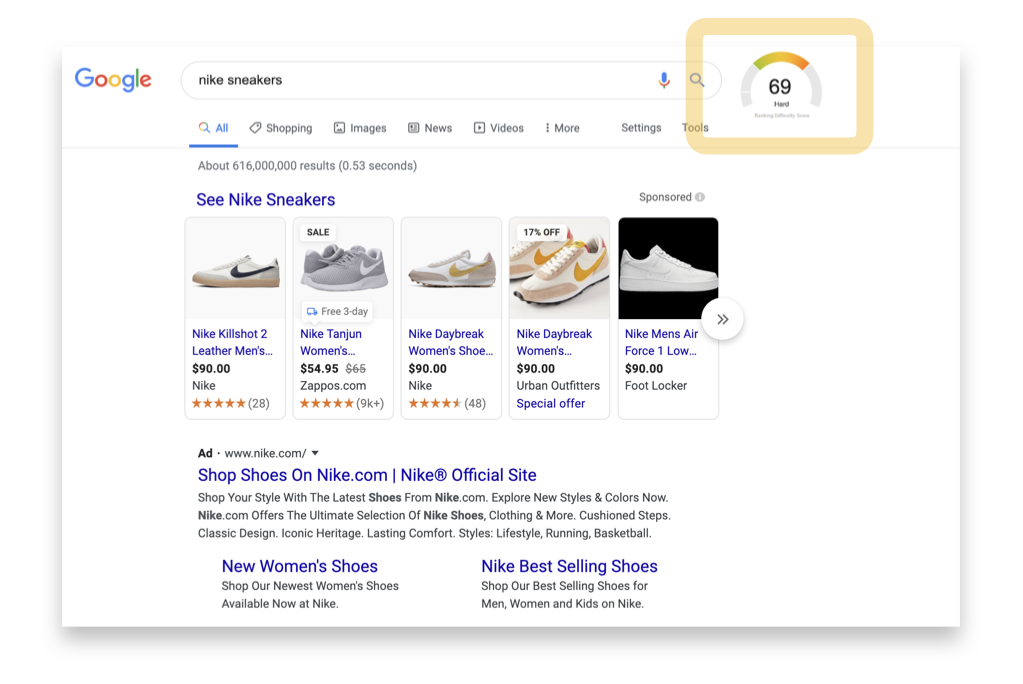
2. Verifying Search Volume and Difficulty Using Tools
You can get a rough estimate of the search volume for a keyword using Google’s Keyword Planner.
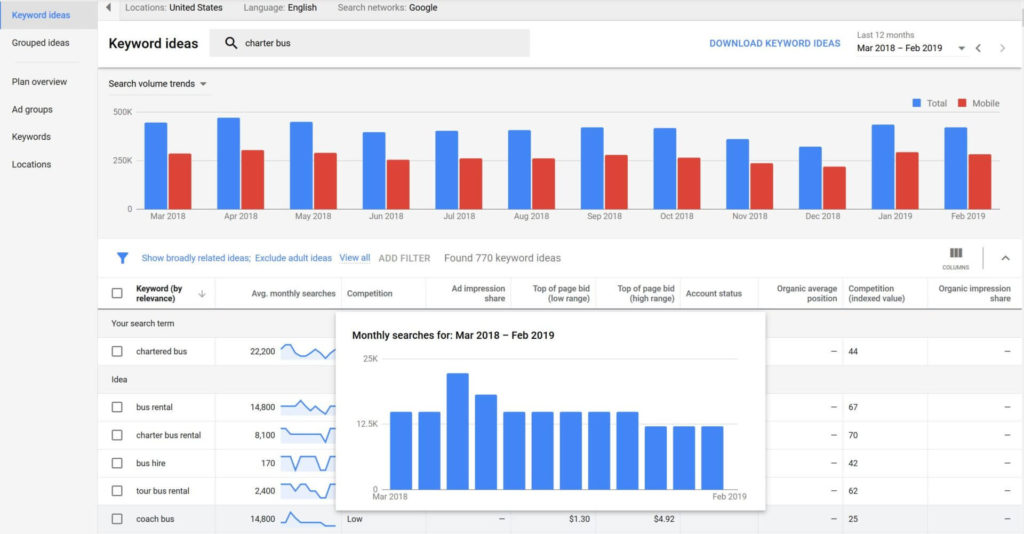
It’s completely free to use Google’s Keyword Planner and it’s where a lot of new digital marketers and SEOs start. But it’s not the easiest tool to use, and it doesn’t produce the other helpful information you need.
There are plenty of tools on the market that makes keyword research easy. So much so that we would go as far as to say that you absolutely have to use a keyword research tool, otherwise, you’re going to miss keywords that you should be targeting. You’ll also try and rank for keywords that are too difficult and fall into the other traps that hold people back.
We created GrowthBar to address all the pain points people—including ourselves—had when doing keyword research.
All you have to do is type your keywords into Google, just as you would if you were performing a search. With the GrowthBar extension enabled, you’ll now see the monthly estimated search volume, a difficulty rating for the keyword, and a list of suggested keywords related to the one you typed in. The web version of GrowthBar also has an easy keyword research feature.
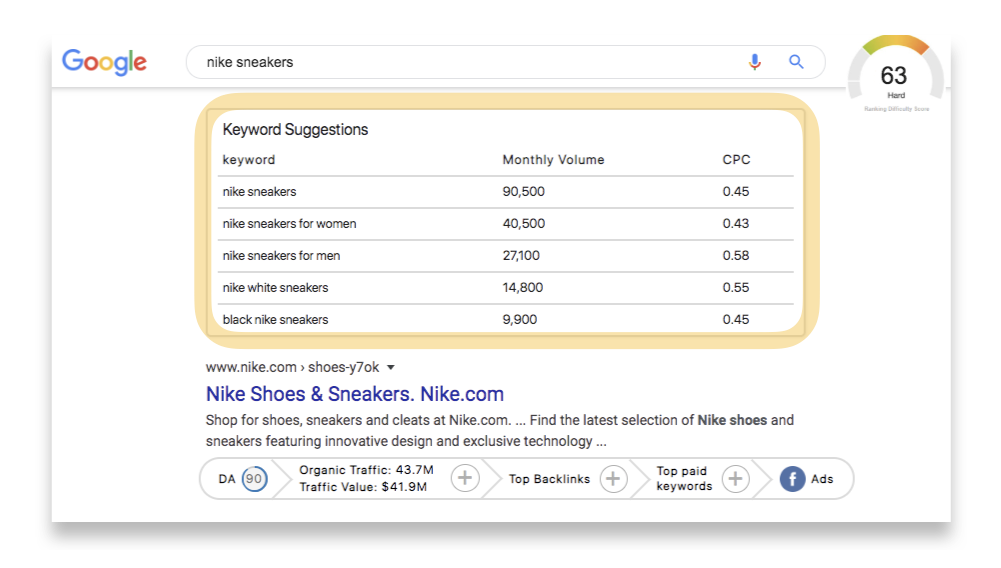
Great SEO tools should spit out keyword suggestions that are long-tail rather than super competitive head terms.
More long-tail keyword examples include:
- “Best Chromebook under $300.”
- “Dentists in Albuquerque”
- “The best gifts for teenage girls”
- “SEO for doctors”
- “How to invest in real estate in San Francisco”
Keep in mind, the key is to find a keyword relevant to your business, with good search volume and a low difficulty score. You’ll have to start with low competition keywords (long-tail), but as your site ages and gains authority, you’ll be able to target more difficult keywords.
3. Titles, Tags, and URLs
The reason why keywords are so important is that this is what Google uses to understand your content.
Titles, known as meta title tags, are among the strongest SEO ranking factors on a page. Best SEO practice entails putting your keyword in the:
- Title tag of your page
- URL slug
- Other meta tags
So if you’re trying to rank for the query “beginner’s guide to SEO,” you’ll want to be sure those keywords appear in your title and URL, as this blog post does!
4. Optimizing Your Content
Choosing the right keywords you want to rank for is only part of the process. Without an awesome piece of content that’s going to provide the answers your customers are looking for—and is well optimized for search engines—you’re not going to rank.
So what are some things you should do to make sure your content is optimized for SEO? Here are some:
- Include your target keyword(s) in your content. Keyword density is the concept of percentage of text containing a target keyword out of the total word count of an article. There’s no hard and fast rule for keyword density, but in general you should try and use your target keyword once for every 200 or 300 words.
- Make your content readable by using conversational wording, varying sentence lengths, and include plenty of spacing to make your content consumable on mobile devices. You should also use headers (h1s, h2s, h3s, etc.), bulleted lists, and tables.
- Make your content engaging by using rich images, infographics, and even video. You will curry favor with Google if your content keeps users on-page longer. So the more engaging, the better.
- Optimize images by naming them with your target keyword(s) in mind. Also, use alt text so that web crawlers and users can easily read the content of your images.
- Link to other posts and articles throughout your content. Internal linking is an important part of any SEO strategy. By linking to other content on your site, you will keep users on page and create a richer experience for them. You should also link to other credible websites when appropriate. This shows Google you care about the quality of your content and are only giving users the best information.
Additional reading: Learn more about How to Write a Blog Post for SEO here.
5. Site Speed, UI and Other “Intangibles”
Would you rather use a slow website with an outdated theme or a lightning fast site with a great user interface (UI)? Again, Google is always trying to give Googlers the best possible experience. So I’d be remiss not to underscore the importance of intangibles when it comes to your site’s SEO.
Site speed
Site speed is an important part of any good web experience. In fact, the number of people who bounce off of your site will increase dramatically the slower your webpage loads.
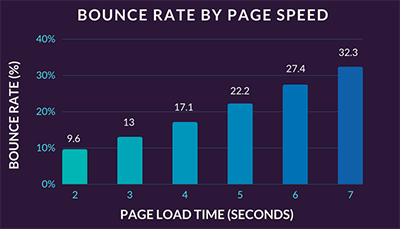
As such, you should ensure your site is reasonably fast. The good news is that most modern hosting platforms and website builders like Bluehost and Shopify are fast enough to host most simple websites. In other words, if you’re just starting out, you shouldn’t have to concern yourself much with site speed. However, if you are noticing a slowdown, you can take a few steps to increase your speed:
- Compress all of your images using a simple image compressor like ImageOptim.
- Install a lazy load plugin, which will make it so that images and other rich content on your site will only load when a user scrolls down the page. Therefore, your webpage will not have to load everything all in the beginning of a user’s session.
- Use a CDN. CDNs, or content delivery networks like Cloudflare allow you to load your content dynamically via other servers. This reduces the weight on your server and should theoretically make everything load faster.
- If your site is still too slow after all this, you may need to upgrade your web hosting.
User Interface (UI)
User interface (UI) and user experience (UX) impact SEO. Your site’s UI design should be clean and functional in order to maximize your website’s SEO value. Again, that’s because websites that are easy on the eyes and easy to navigate tend to keep users on-page longer than ones that do not. Some ways to do this are:
- Stick to a simple, clean web design. Use a template! WordPress, Wix, Shopify, and nearly every other site builder have templates that make it easy for you to plug and play. Don’t try and create your own template from scratch. It’s a waste of money and likely will not be as clean and simple as out-of-the-box designs.
- Adhere to the “3 click design” rule. While this rule certainly isn’t hard and fast, in general a user should be able to get from one page to any other page on a website by clicking no more than three times. This means your website hierarchy and navigation should be intuitive and easy.
- Always look for ways to improve user experience. If you think a simple design element makes something easier to read or will keep users on-page longer, it probably will. For instance, I love tables of contents at the beginning of my blog posts. It makes posts more digestible and are useful to readers looking to skim.

Note: What works for one search vertical doesn’t always work for another. If you’re looking for NFT SEO, pages with slick UI and user-generated reviews will rank at the top of Google, but if you’re researching the best outfit to wear to the prom, you’re more likely to see long-form blog post with beautiful fashion images at the top of Google.
Off-Page SEO: Building Links and Sending Signals
Creating the best article you can by thoroughly answering the query and optimizing your content perfectly for search engines doesn’t mean you’ll rank on the first page of Google every time.
Unless you’re in a niche with very little competition, you’ll likely have competitors also targeting the same keywords as you. So, how do you rank higher than the competitors that were already there before you?
Build links to your site!
More commonly referred to as backlinks or inbound links, links are HTML hyperlinks that direct people from one site to another. They are the currency of the internet. When someone links to another site, Google sees this as a kind of vote of confidence. This makes sense because you wouldn’t link to another site that you didn’t recommend, right?
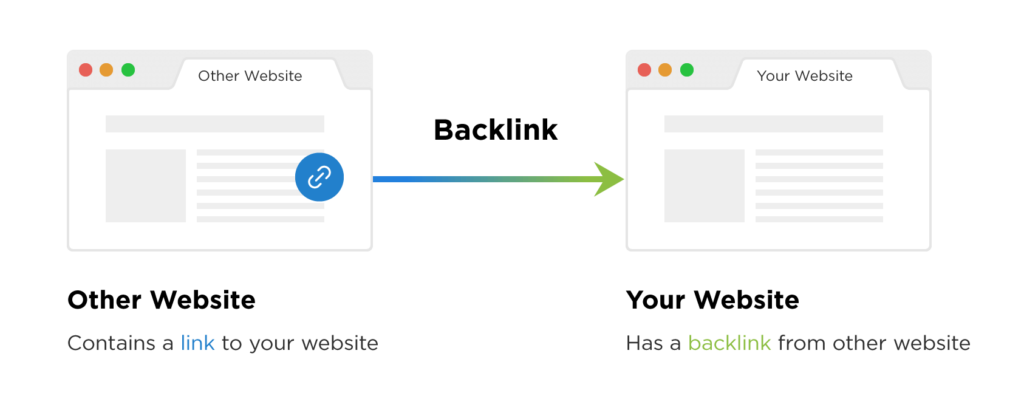
When people talk about off-page SEO, they’re primarily talking about backlinks.
Especially for new websites, backlinks are supremely important. They’re the only way Google knows that your website is trustworthy enough to send traffic to.
To proactively build backlinks, some of the things you can do is:
- PR! Put out press releases and curry favor with journalists in your industry
- Reach out to other sites and ask to guest post on their site
- Share your content across social media platforms
- Create sharable resources on your pages, such as infographics, charts, and interesting statistics
- Contact media outlets and ask for exposure
Building backlinks is a deep topic. It’s not something we will dive too far into in this post, as it’s more on the advanced side of SEO than it is for beginners. But suffice it to say, if you’re going to take SEO seriously you should learn about it!
Additional reading: Learn more about backlinking with The Ultimate Guide to Backlinking for SEO.
Wrapping Up
We hope you enjoyed this beginner’s guide to SEO—and more importantly, you’re now confident you understand what SEO is and how you can apply it to your own site, whether you have a site for crypto buyers or are a SaaS agency.
We appreciate it’s a lot to take in, but it really boils down to just a few key things to focus on:
- Keyword research
- Optimizing your content for your keywords
- Promoting your content and attracting links from other sites
Google has confirmed that quality content and links are the two strongest ranking factors. It’s no secret that these two things move the needle the most.
If you keep improving on these basic SEO principles, you’ll keep seeing improvements in your site’s rankings.




